Difference between revisions of "KAmod Motor Driver"
(→BRK/FRE – Wybór sposobu zatrzymania) |
(→Przyciski szybkiego testowania) |
||
| Line 198: | Line 198: | ||
</center> | </center> | ||
| − | ===== | + | ===== Quick test buttons ===== |
<center> | <center> | ||
{| class="wikitable" style="width: 1000px;" | {| class="wikitable" style="width: 1000px;" | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | ! style="text-align: center;"| | + | ! style="text-align: center;"|Type |
| − | ! style="text-align: center;"| | + | ! style="text-align: center;"|Function |
|- | |- | ||
| style="text-align: center;"|<b>TEST</b> | | style="text-align: center;"|<b>TEST</b> | ||
| − | + | Microswitch buttons | |
| style="text-align: left;"| | | style="text-align: left;"| | ||
| − | * | + | * Setting the output power to 100%, regardless of the signal level on the <b>ADJ IN</b> connector |
| − | * | + | * Changing the direction of rotation when the <b>DIR</b> connector is not driven |
|} | |} | ||
</center> | </center> | ||
| − | + | The KAmod Motor Driver can be easily tested without applying control signals, using two miniature buttons located on the board: | |
| − | :* <b>TEST RUN</b> – | + | :* <b>TEST RUN</b> – pressing the button sets the output power to 100%, regardless of the signal level on the ADJ IN connector; |
| − | :* <b>TEST DIR</b> – | + | :* <b>TEST DIR</b> – pressing the button changes the direction of rotation if the DIR connector is not controlled by an external signal. |
| − | |||
<br><br> | <br><br> | ||
<center> | <center> | ||
Revision as of 12:56, 18 June 2024

Contents
- 1 Description
- 2 Basic features and parameters
- 3 Standard equipment
- 4 Electrical schematics
- 5 Output power control
- 6 Selection of the control signal amplitude range
- 7 Output polarity control (direction of motor rotation)
- 8 Forcing the engine to stop
- 9 BRK/FRE – Wybór sposobu zatrzymania
- 10 Quick test buttons
- 11 Potencjometry do regulacji parametrów pracy
- 12 Sygnalizacja stanu pracy
- 13 Zasilanie i obciążenie
- 14 Wymiary
- 15 Linki zewnętrzne
Description
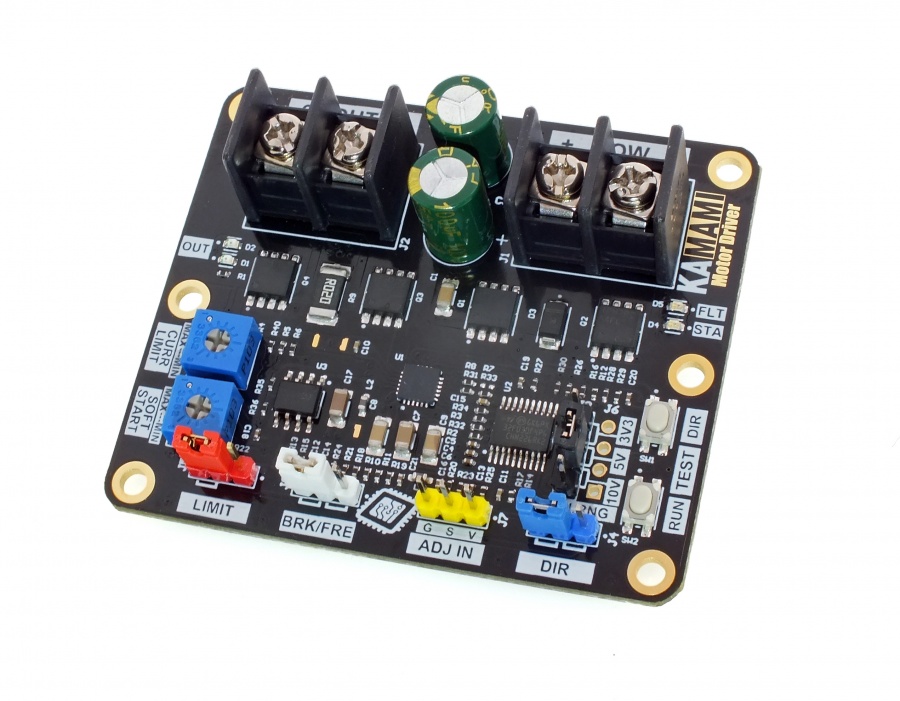
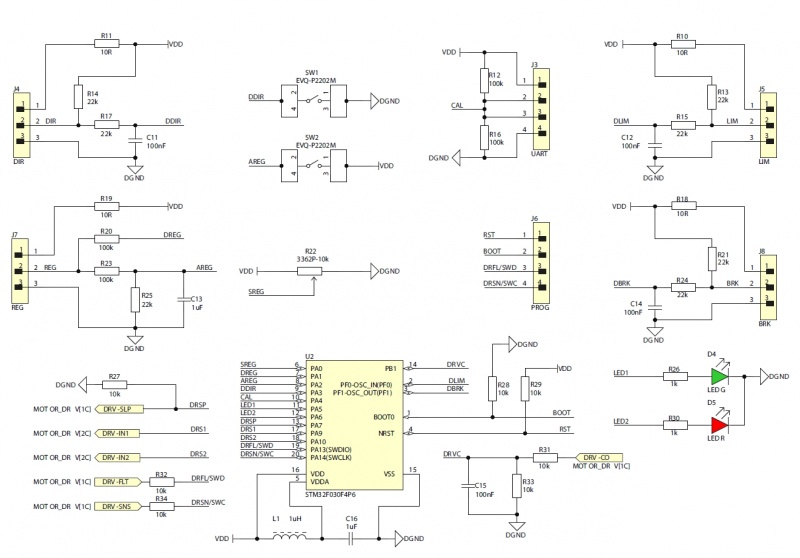
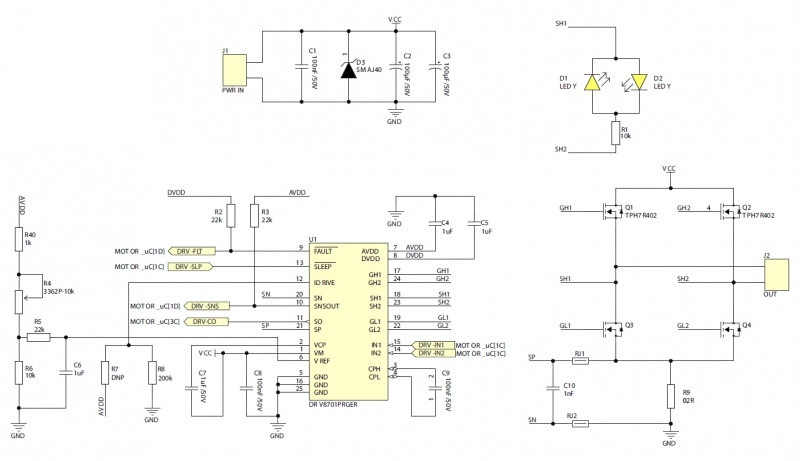
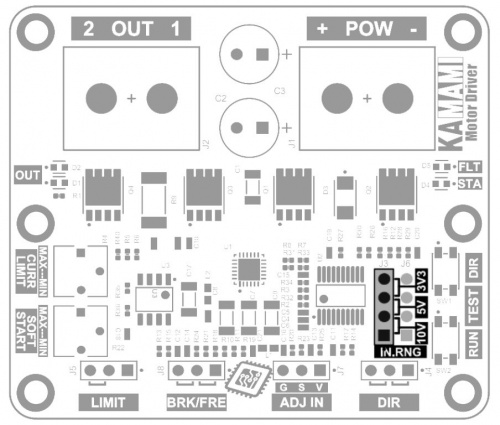
The KAmod Motor Driver is an electric motor controller for DC voltages up to 30 V. It allows the selection of the motor's direction of rotation and the adjustment of its power in the range 0...100%, which in practice is used for speed control. The control signal can be a voltage signal falling within one of 3 ranges: 0...3.3 V, 0...5 V or 0...10 V, or a PWM signal with an amplitude of 3.3 V, 5 V or 10 V. Such signals can be easily obtained from Raspberry, Arduino, Nucleo boards or from a simple potentiometer. The power stage is built with MOSFET transistors connected in an H-bridge arrangement, which ensures high output power and high efficiency of the controller.
Basic features and parameters
- Regulates motor power using PWM method
- Allows motor operation in both directions
- Motor power can be controlled by analogue or digital signal.
- Analogue control signal can be in one of 3 ranges: 0...3.3 V, 0...5 V or 0...10 V
- A digital control signal in the form of a PWM waveform should have a frequency in the range of 200 Hz... 50 kHz and an amplitude of 3.3 V, 5 V or 10 V.
- Separate digital input to control the direction of motor rotation.
- Soft start and soft stop function.
- Stop function with limit sensor signal
- Stop function with or without blocking of the motor shaft
- Output frequency of PW signal
- PWM output signal frequency: 750 Hz.
- Overload protection (output current limitation).
- Protection against overheating
- DC voltage supply in the range 6...30 V
- Maximum continuous motor current: 15 A
- Buttons for quick testing
- LEDs to indicate the operating status of the unit
Standard equipment
| Code | Description |
|---|---|
| KAmod Motor Driver | Assembled and launched module |
Electrical schematics
Output power control
| Connector | Function |
|---|---|
| ADJ IN
Goldpin pins 3x1, 2,54 mm |
|
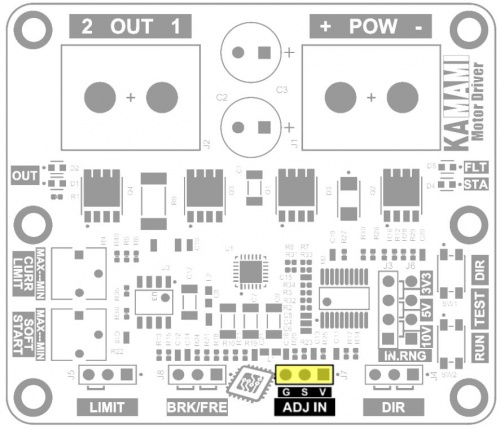
The ADJ IN connector pins perform the following functions:
- V (pin 1, right) – 3.3 V voltage output that can be loaded with a current of up to 10 mA;
- S (pin 2, middle) – analog or digital signal input, the maximum input voltage cannot exceed 16V;
- G (pin 3, left) –ground of the system, the ground of the control signal should be connected.
The supplied analog signal must be in one of the 3 control ranges: 0...3.3 V; 0...5 V or 0...10 V. The output power of the motor controller will be proportional to the voltage applied to the S contact and depends on the selected control range. You can connect an ordinary potentiometer to the V, S, G contacts of the connector and thus regulate the output power.
Digital signal - PWM can have a frequency ranging from 200 Hz to 50 kHz, a duty cycle ranging from 0 to 100% and an amplitude of 3.3 V, 5 V or 10 V. The output power of the motor controller will be proportional to the duty cycle of the PWM signal .
The control range for both analog and digital signals is selected using the IN.RNG connector.
Selection of the control signal amplitude range
| Connector | Function |
|---|---|
| IN.RNG
Goldpin pins 4x1, 2.54 mm |
|
The control signal fed to the ADJ IN connector may come from various systems, development boards and SBC computers. The two most popular standards for the voltage level of digital systems are 3.3 V and 5 V. The analog signal used in home and industrial automation systems is a signal in the range of 0...10 V. In order for the KAmod Motor Driver to work properly with various systems, it must be set the correct voltage range for the control signal. The IN.RNG (input range) connector is used for this purpose.
Setting the jumper in one of 3 positions allows you to select 1 of 3 ranges:
- valve on pins 1-2: voltage range for the control signal is 10 V;
- valve on pins 2-3: voltage range for the control signal is 5 V;
- valve on pins 3-4: voltage range for the control signal is 3.3 V.
The jumper position and corresponding voltage ranges are clearly marked on the motor controller board.
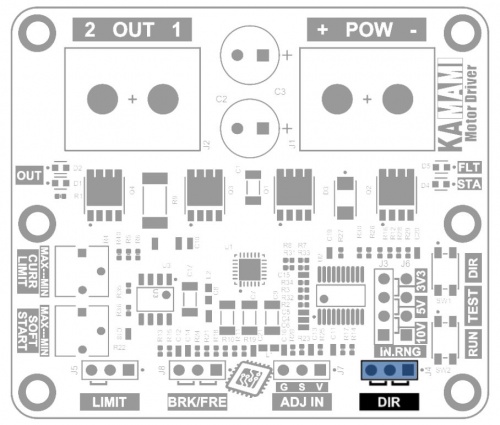
Output polarity control (direction of motor rotation)
| Connector | Function |
|---|---|
| DIR
Goldpin pins 3x1, 2.54 mm |
|
The direction of rotation of a typical DC motor depends on the polarity of the voltage supplying the motor. By reversing the polarity of the voltage, you can reverse the direction of motor rotation. The KAmod Motor Driver allows you to select the direction of motor rotation using the state on the DIR connector.
Setting the jumper in one of two positions allows you to select one of two directions - the polarity of the output voltage:
- valve on pins 1-2 (on the right side): there will be a positive potential at the OUT 1 output, and a power supply ground at the OUT 2 output;
- valve on pins 2-3 (on the left): the OUT 1 output will have a power supply ground, and the OUT 2 output will have a positive potential.
The DIR connector pins perform the following functions:
- pin 1 (right) – 3.3 V voltage output, which can be loaded with a current of up to 10 mA;
- pin 2 (middle) – input of a digital signal determining the direction;
- pin 3 (left) – ground of the system, connect the ground of the control signal.
The DIR input is normally pulled up to 3.3V (pull-up). The state will change after applying ground to pin 2 or shorting pins 2-3. Voltage up to 6 V can be supplied to the input.
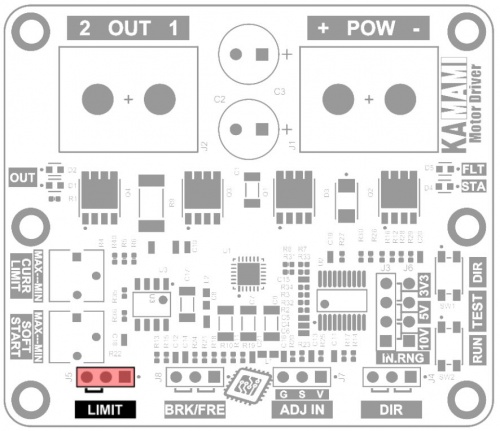
Forcing the engine to stop
| Connector | Function |
|---|---|
| LIMIT
Goldpin pins 3x1, 2.54 mm |
|
Engine operation can be interrupted at any time. The output power is then set to 0% regardless of the control signal supplied to the ADJ IN input. After stopping using the LIMIT connector, restarting the engine is possible when one of 2 conditions is met:
- the direction of rotation will be changed by changing the state on the DIR connector. The motor will start running in the opposite direction even if the LIMIT signal remains active when the direction is reversed.
- the control signal on the ADJ IN connector will reach zero and the signal on the LIMIT connector will become inactive. After increasing the signal at the ADJ IN connector again, the motor will start running in any direction you set.
The state on the LIMIT connector is:
- active when pins 2-3 (left side) are shorted;
- inactive when pins 1-2 (right side) are shorted, or no pins are shorted.
The LIMIT connector pins perform the following functions:
- pin 1 (right) – 3.3 V voltage output, which can be loaded with a current of up to 10 mA;
- pin 2 (middle) – digital signal input activating the stop function;
- pin 3 (left) – ground of the system, connect the ground of the control signal.
The LIMIT input is normally pulled up to 3.3V (pull-up). The active state will occur after applying ground to pin 2 or shorting pins 2-3. Voltage up to 6 V can be supplied to the input.
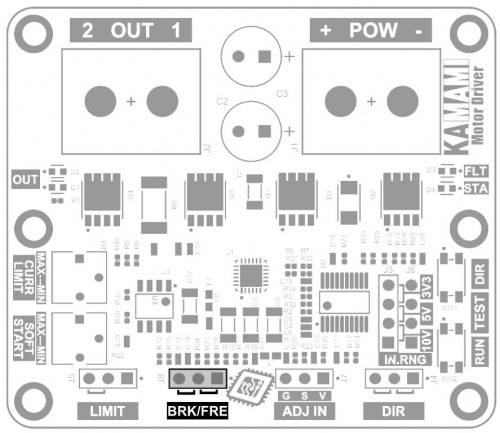
BRK/FRE – Wybór sposobu zatrzymania
| Connector | Function |
|---|---|
| BRK/FRE
Goldpin pins 3x1, 2.54 mm |
|
Stopping the engine using the LIMIT connector can be done in two ways:
- freely,
- with braking.
The BRK/FRE connector status allows you to select one of these options:
- free stop - shorted pins 1-2 (right side). Power to the motor is disconnected and the motor decelerates to a stop;
- stop with braking - pins 2-3 shorted (on the left). The motor's power is disconnected and its power terminals are shorted to ground, causing the motor to suddenly decelerate.
The activated stop function with braking means that when there is a zero control signal on the ADJ IN connector, the motor is also blocked - its power terminals are shorted to ground, which makes it much more difficult to rotate it using an external force.
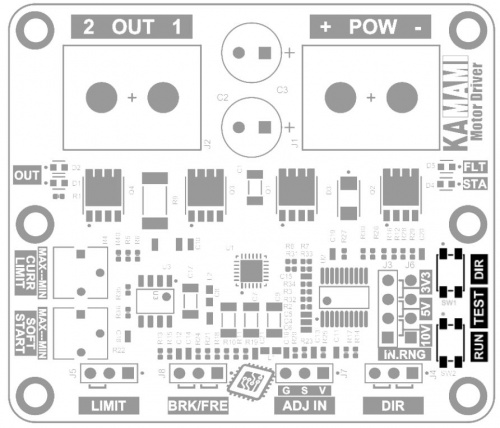
Quick test buttons
| Type | Function |
|---|---|
| TEST
Microswitch buttons |
|
The KAmod Motor Driver can be easily tested without applying control signals, using two miniature buttons located on the board:
- TEST RUN – pressing the button sets the output power to 100%, regardless of the signal level on the ADJ IN connector;
- TEST DIR – pressing the button changes the direction of rotation if the DIR connector is not controlled by an external signal.
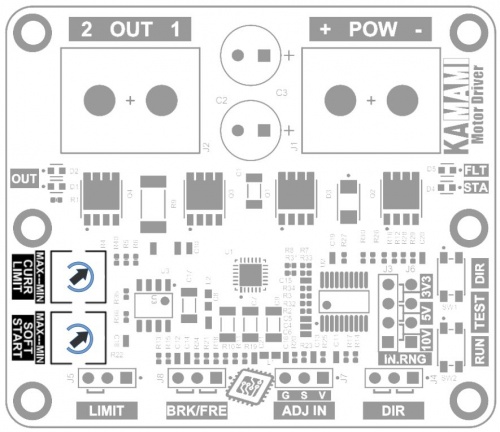
Potencjometry do regulacji parametrów pracy
| Typ | Funkcja |
|---|---|
| SOFT START CURR LIMIT Potencjometry miniaturowe |
|
Sterownik silnika KAmod Motor Driver realizuje funkcję SOFT START, która obejmuje:
- łagodny rozruch,
- łagodne zwiększanie prędkości,
- łagodne zmniejszanie prędkości,
- płynną zmianę kierunku obrotów (z etapami łagodnego hamowania, zatrzymania i łagodnego rozruchu).
Działanie tych rozwiązań pozwala zmniejszyć obciążenie źródła zasilania oraz ograniczyć przeciążenia mechaniczne silnika i elementów mechanicznych połączonych z silnikiem. Intensywność działania powyższych funkcji określa położenie potencjometru oznaczonego SOFT START. W zakresie od pozycji MIN do MAX czas rozruchu z poziomu 0% do 100% jest regulowany w zakresie od 1 do 4 sekund.
Sterownik silnika KAmod Motor Driver realizuje funkcję zabezpieczenia przed przeciążeniem CURRENT LIMIT, która zabezpiecza sterownik oraz silnik przed przepływem zbyt dużego prądu (funkcja nie gwarantuje zabezpieczenia przed zwarciem na wyjściu sterownika). Poziom ograniczenia pądu określa położenie potencjometru oznaczonego CURR LIMIT. W zakresie od pozycji MIN do MAX wartość prądu jest regulowana od ok. 2 A do ok. 15 A. Działanie ograniczenia jest sygnalizowane miganiem czerwonej diody sygnalizacyjnej FLT.
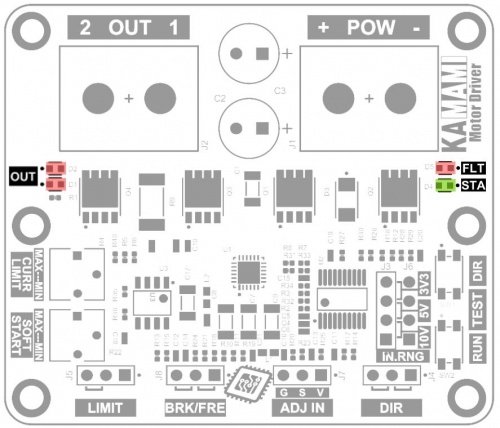
Sygnalizacja stanu pracy
| Typ | Funkcja |
|---|---|
| OUT FLT STA Diody LED |
|
OUT (Output) - Sygnalizacja napięcia wyjściowego jest realizowana przy pomocy dwóch diod LED oznaczonych na płytce sterownika jako OUT. Każda z diod odpowiada jednemu kierunkowi obrotów, jednak w przypadku silników o dużej mocy, energia indukowana w silniku w trakcie sterowania PWM będzie powodowała efekt świecenia obu diod jednocześnie. Diody będą świeciły tym jaśniej, im większy będzie stopień wysterowania wyjścia.
STA (Status) - W czasie normalnej pracy sterownika zielona dioda STA świeci światłem ciągłym. Gdy zostanie wymuszone zatrzymanie silnika sygnałem na złączu LIMIT, wówczas dioda STA będzie świeciła krótkimi impulsami, sygnalizując w ten sposób, że należy spełnić jeden z warunków zakończenia stanu zatrzymania, aby uruchomić silnik.
FLT (Fault) - W czasie normalnej pracy czerwona dioda FLT jest wygaszona. Świecenie diody krótkimi impulsami oznacza działanie zabezpieczenia przed przeciążeniem CURRENT LIMIT, czyli ograniczenie prądu zasilającego silnik. Świecenie ciągłe diody FLT oznacza wyłączenie sterownika z powodu przeciążenia i/lub przegrzania.
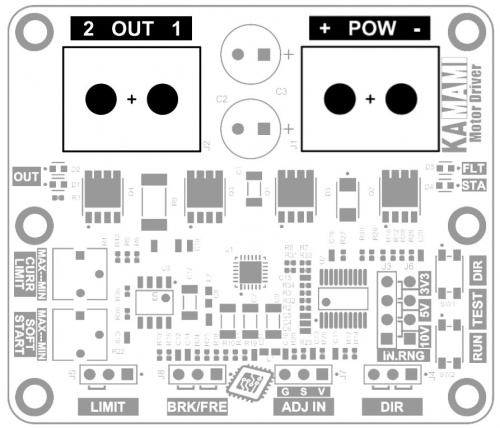
Zasilanie i obciążenie
| Złącze | Funkcja |
|---|---|
| POW OUT Złącze śrubowe DG35, M3 22...12AWG |
|
POW - Napięcie zasilania dołączone do złącza POW musi zawierać się w zakresie 6...30 V. Służy ono do zasilania sterownika silnika oraz dołączonego do jego wyjścia obciążenia, np silnika. W przypadku obciążeń o dużej mocy należy zapewnić źródło zasilania o odpowiedniej wydajności. Złącze wyposażone jest w śruby rozmiaru M3.
OUT - Złącze umożliwiające dołączenie obciążenia, np. silnika elektrycznego na napięcie stałe, itp. Napięcie znamionowe silnika musi odpowiadać wartości napięcia zasilającego sterownik. Prąd znamionowy silnika nie powinien przekraczać 15 A. Złącze wyposażone jest w śruby rozmiaru M3.
W przypadku obciążeń o dużej mocy należy zadbać o odpowiednio dużą średnicę oraz jak najmniejszą długość przewodów połączeniowych.
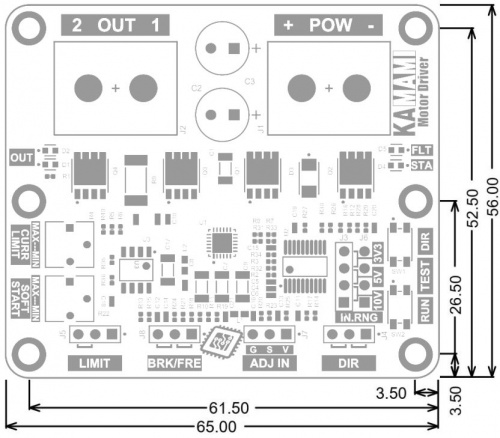
Wymiary
Płytka sterownika silnika KAmod Motor Driver ma wymiary 65x56 mm i wysokość ok. 21 mm. Umiejscowienie otworów mocujących pokazano na rysunku.