KAmod RPI 485 CAN Hat: Difference between revisions
From Kamamilabs.com - Wiki
| (2 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 402: | Line 402: | ||
</center> | </center> | ||
===== <b> | ===== <b>Startup </b>===== | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
Start Raspberry Pi 5 with the operating system installed on the memory card or other media. After the system desktop is displayed, open the console window (Terminal), e.g. using the Ctrl+Alt+T key combination and enter:<br> | |||
'''<pre style="color: blue">sudo nano /boot/firmware/config.txt</pre>''' | '''<pre style="color: blue">sudo nano /boot/firmware/config.txt</pre>''' | ||
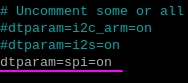
( | (in earlier versions of the operating system, the config.txt file was placed directly in the /boot directory)<br><br> | ||
In the file whose content we will see, remove the comment (remove the # sign) from the line: | |||
'''<pre style="color: blue">dtparam=spi=on</pre>''' | '''<pre style="color: blue">dtparam=spi=on</pre>''' | ||
However, if there is no such line, you should add it. <center> | |||
<center> | |||
[[File:KAmod-MultiBus-Hat config 1.jpg|none|800px|thumb|center]] | [[File:KAmod-MultiBus-Hat config 1.jpg|none|800px|thumb|center]] | ||
</center> | </center> | ||
Then at the end of the file (scroll to the bottom with the arrows) add the following lines:<br> | |||
'''<pre style="color: blue">dtoverlay=mcp2515-can0,oscillator=16000000,interrupt=25,spimaxfrequency=10000000</pre>''' | '''<pre style="color: blue">dtoverlay=mcp2515-can0,oscillator=16000000,interrupt=25,spimaxfrequency=10000000</pre>''' | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
and | |||
'''<pre style="color: blue">dtoverlay=sc16is752-spi1,int_pin=24</pre>''' | '''<pre style="color: blue">dtoverlay=sc16is752-spi1,int_pin=24</pre>''' | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
| Line 423: | Line 422: | ||
[[File:KAmod-MultiBus-Hat_config_2.jpg|none|800px|thumb|center]] | [[File:KAmod-MultiBus-Hat_config_2.jpg|none|800px|thumb|center]] | ||
</center> | </center> | ||
Then save the changes using the Ctrl+O keys, close the editor using the Ctrl+X keys and restart the system, e.g. by entering the command:<br> | |||
'''<pre style="color: blue">sudo reboot</pre>'''<br> | '''<pre style="color: blue">sudo reboot</pre>'''<br> | ||
After the system desktop is displayed, open the console window (Terminal), e.g. using the Ctrl+Alt+T key combination and enter: | |||
'''<pre style="color: blue">sudo dmesg | grep -i spi</pre>'''<br> | '''<pre style="color: blue">sudo dmesg | grep -i spi</pre>'''<br> | ||
If the previous steps were performed correctly, the following summary should be displayed: | |||
<center> | <center> | ||
[[File:KAmod-MultiBus-Hat_config_3.jpg|none|800px|thumb|center]] | [[File:KAmod-MultiBus-Hat_config_3.jpg|none|800px|thumb|center]] | ||
</center> | </center> | ||
This means that both the SC16IS762 and MCP2515 controllers have been correctly installed in the system.<br><br> | |||
Testing the CAN interface requires entering 3 commands: | |||
'''<pre style="color: blue">sudo ip link set can0 up type can bitrate 1000000 | '''<pre style="color: blue">sudo ip link set can0 up type can bitrate 1000000 | ||
sudo ifconfig can0 up | sudo ifconfig can0 up | ||
cansend can0 000#11.22.33.44</pre>'''<br> | cansend can0 000#11.22.33.44</pre>'''<br> | ||
The D10 LED should flash, indicating activity on the CAN bus.<br> | |||
RS485 interfaces can be tested using the minicom, for RS485-1 enter: | |||
'''<pre style="color: blue">minicom -D /dev/ttySC0</pre>'''<br> | '''<pre style="color: blue">minicom -D /dev/ttySC0</pre>'''<br> | ||
while for RS485-2 enter: | |||
'''<pre style="color: blue">minicom -D /dev/ttySC1</pre>'''<br> | '''<pre style="color: blue">minicom -D /dev/ttySC1</pre>'''<br> | ||
The minicom program allows you to send characters entered from the keyboard and displays characters received via the selected RS485 interface. During the interface activity, the D5/D7 diodes will flash, but at high transmission speeds, e.g. 115200, the flashing of the LEDs will be barely noticeable. | |||
<br><br> | <br><br> | ||
===== <b> | ===== <b>Links </b>===== | ||
*[https://wiki.kamamilabs.com/images/8/83/MCP2515.pdf | *[https://wiki.kamamilabs.com/images/8/83/MCP2515.pdf Datasheet MCP2515 ] | ||
*[https://wiki.kamamilabs.com/images/c/cb/SC16IS752_SC16IS762.pdf | *[https://wiki.kamamilabs.com/images/c/cb/SC16IS752_SC16IS762.pdf Datasheet SC16IS762IPW] | ||
*[https://wiki.kamamilabs.com/images/0/0a/ADM2483.pdf | *[https://wiki.kamamilabs.com/images/0/0a/ADM2483.pdf Datasheet ADM2483] | ||
*[https://wiki.kamamilabs.com/images/f/fd/TJA1052IT.pdf | *[https://wiki.kamamilabs.com/images/f/fd/TJA1052IT.pdf Datasheet TJA1052] | ||
*[https://wiki.kamamilabs.com/images/3/35/Tps5401.pdf | *[https://wiki.kamamilabs.com/images/3/35/Tps5401.pdf Datasheet TPS5401] | ||
*[https://wiki.kamamilabs.com/images/2/25/KAmod-MultiBus-Hat_3d.zip Model | *[https://wiki.kamamilabs.com/images/2/25/KAmod-MultiBus-Hat_3d.zip CAD Model (STEP)] | ||
Latest revision as of 06:41, 3 June 2025

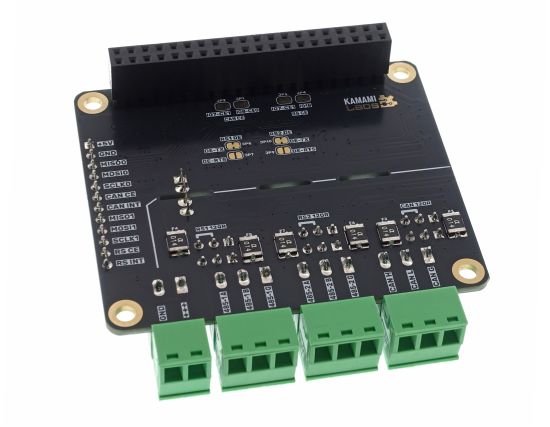
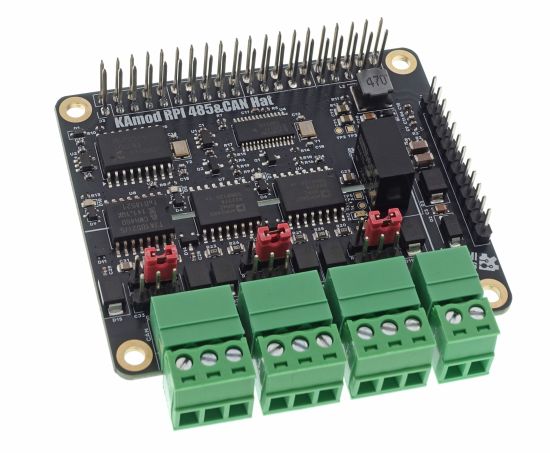
Description
KAmod RPI 485&CAN Hat - Module with two RS485 interfaces and a CAN interface for Raspberry Pi
KAmod RPI 485&CAN Hat allows you to easily expand Raspberry Pi 5 computers with two RS485 interfaces and one CAN 2.0B interface. The interfaces contain extensive protection circuits and are galvanically isolated from the control circuits, which guarantees stable operation and resistance to interference and failures. The module has been designed to be compatible with Raspberry Pi series boards not only in version 5. It is controlled via 2 SPI interfaces, available on the 40-pin RPi connector, and in many other boards, e.g. Arduino, STM32, etc.
Basic features and parameters
- 2 RS485 interfaces – controlled by SC16IS752 controller (SPI→2xUART)
- 1 CAN 2.0B interface – controlled by MCP2515 controller (SPI→CAN)
- RS485 interfaces equipped with 2 isolated ADM2483 transceivers
- CAN interface equipped with isolated TJA1052 transceiver
- RS485 and CAN interfaces galvanically separated from control circuits
- Possibility to connect 120 Ω terminating resistors to each interface line
- Maximum RS485 interest communication speed: 500 kbps
- Maximum CAN interest communication speed: 1 Mbps
- Control via two SPI interfaces operating with 3.3 V voltage
- Automatic control of RS485 transceiver transmission direction
- Power supply 5 V/0.3 A taken from the Raspberry Pi board or from an additional source
- Optional power input adapted to a voltage in the range of 8...32 V
- Stabilized power output 5 V, max 0.5 A
- Easy installation on Raspberry Pi 5, also in the version with the RPi Active Cooler radiator
- Can work with many boards from the Raspberry Pi family and others equipped with SPI interfaces operating at a voltage of 3.3 V
- Module dimensions 65x56 mm, height approx. 15 mm (and a connector under the board with a height of approx. 13 mm)
Standard Equipment
| Code | Description |
|---|---|
| KAmod RPI 485&CAN Hat |
|
| Mounting Kit |
|

Block diagram
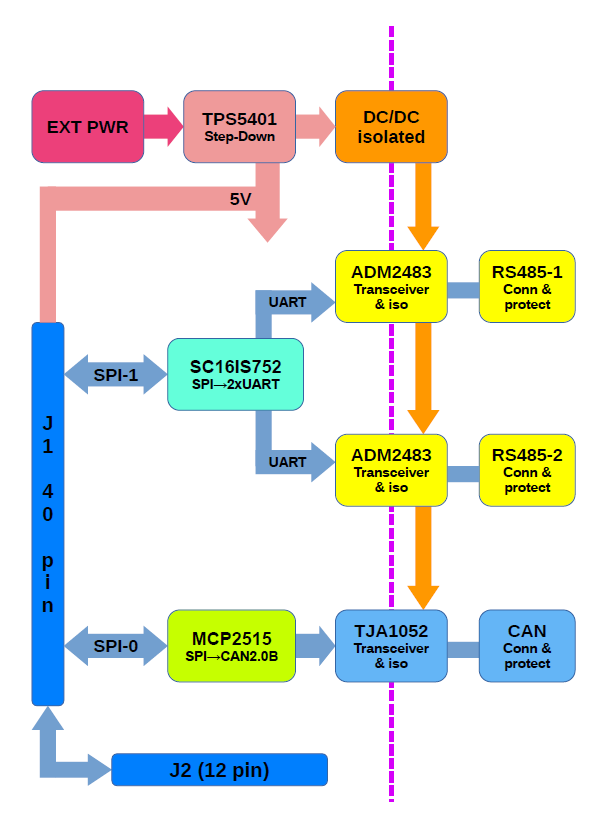
Circuit diagram
The circuit diagram of the KAmod RPI 485&CAN Hat module can be downloaded here: KAmod RPI 485&CAN Hat diagram
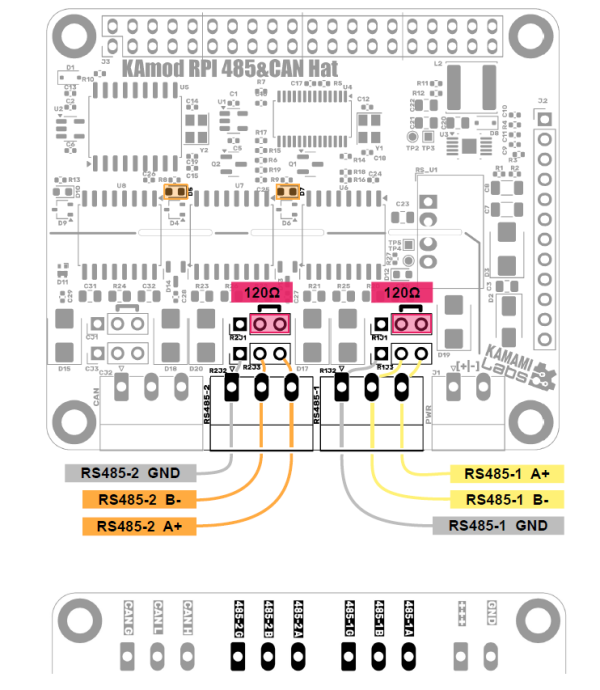
RS485 Interfaces
| Interface | Element | Function |
|---|---|---|
| RS485-1 |
Connector |
Connecting a 120 Ω terminating resistor to the RS485-1 bus line, |
|
Connector |
Main RS485-1 bus connector, pin 1 – GND; pin 2 – B(-); pin 3 – A(+) | |
|
Connector |
Additional RS485-1 bus connector, pin 1 – GND; pin 2 – B(-); pin 3 – A(+) | |
|
LED |
The diode lights up to indicate data transmission/reception on the RS485-1 interface signal lines | |
| RS485-2 |
Connector |
Connecting a 120 Ω terminating resistor to the RS485-2 bus line, |
|
Connector |
Main RS485-2 bus connector, pin 1 – GND; pin 2 – B(-); pin 3 – A(+) | |
|
Connector |
Secondary RS485-2 bus connector, pin 1 – GND; pin 2 – B(-); pin 3 – A(+) | |
|
LED |
The diode lights up to indicate data transmission/reception on the RS485-2 interface signal lines |
The RS485 interfaces are controlled by ADM2483 transceivers, which also provide galvanic separation between the control signals and the RS485 bus lines.
The bus lines are marked as: A(+), B(-) and GND ground and are available on the Phoenix MC connector (R1J2, R2J2) and on goldpin pins with a standard 2.54 mm pitch (R1J3, R2J3). Their arrangement is shown in the drawing and is described on the bottom side of the module board.
The RS485 bus lines are equipped with circuits protecting against overvoltages. Putting a jumper on pins 2-3 of RxJ1 allows you to connect a 120 Ω terminating resistor between lines A and B of the interface.
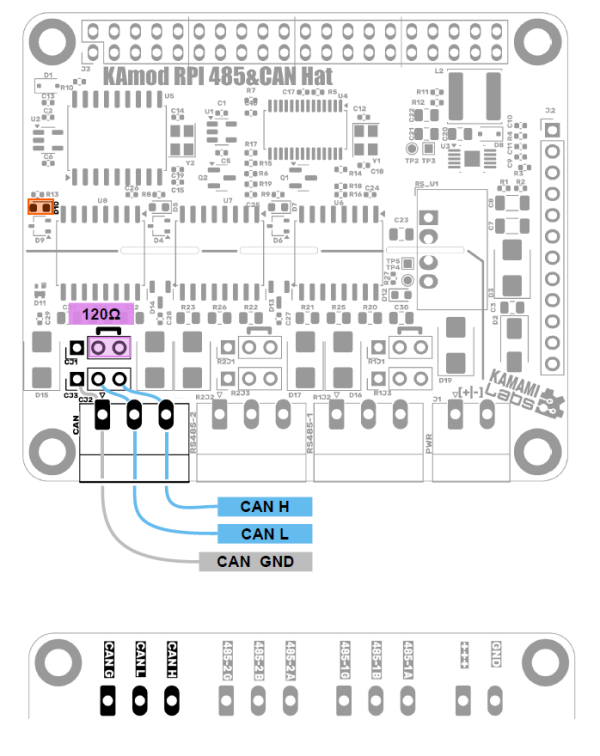
CAN Interface
| Interface | Element | Function |
|---|---|---|
| CAN |
Connector |
Connecting a 120 Ω terminating resistor to the CAN bus line, |
|
Connector |
Main CAN bus connector, pin 1 – GND; pin 2 – CAN L; pin 3 – CAN H | |
|
Connector |
Additional CAN interface connector,
pin 1 – GND; pin 2 – CAN L; pin 3 – CAN H | |
|
LED |
The diode lights up to indicate data transmission/reception on the CAN interface lines |
The CAN interface is controlled by a TJA1052 transceiver, which also provides galvanic separation between control signals and the CAN bus lines.
The bus lines are marked as: CAN H, CAN L and ground GND and are available on the Phoenix MC (CJ2) type connector and on goldpins (CJ3) with a standard 2.54 mm pitch. Their layout is shown in the drawing and is described on the bottom side of the module board.
The CAN bus lines are equipped with circuits that protect against overvoltages. Putting a jumper on pins 2-3 of CJ1 allows you to connect a 120 Ω terminating resistor between the CAN H and CAN L lines.
RS485 Control
| RS485 Interfaces | |
|---|---|
| Control Signal | Function |
| MOSI1 (SPI 1) | SPI data input of SC16IS762 controller, connected to GPIO20 RPi (pin 38 of J3) |
| MISO1 (SPI 1) | SPI data output of SC16IS762 controller, connected to GPIO19 RPi (pin 35 of J3) |
| SCLK1 (SPI 1) | SPI clock input of SC16IS762 controller, connected to GPIO21 RPi (pin 40 of J3) |
| RS CE | SPI interface activation input of SC16IS762 controller |
| By default connected to GPIO07 (pin 26 of J3 connector) - Shorted jumper JP3 | |
| Optionally connected to GPIO18 (pin 12 of J3 connector) - Shorted jumper JP4 | |
| RS INT | SC16IS762 controller IRQ interrupt output connected to GPIO24 (pin 18 of J3 connector) |
All control signals are led out on connector J1 (40-pin, compatible with Raspberry Pi boards) and on pin header J2. The signal layout is shown in the figure below, additionally the signals on connector J2 are described on the bottom side of the KAmod RPI 485&CAN Hat board.
RS485 interfaces are implemented via the SC16IS762 controller, the description of this system is available in the manufacturer's documentation.
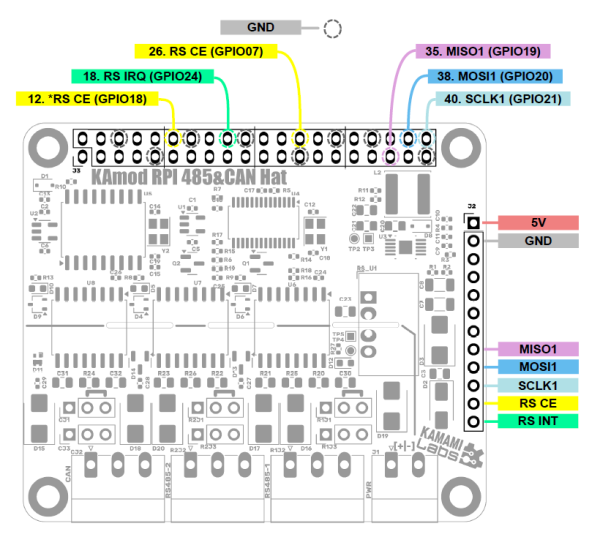
CAN Control
| CAN Interface | |
|---|---|
| Control Signal | Function |
| MOSI0 (SPI 0) | MCP2515 Controller SPI Data Input Connected to GPIO10 RPi (J3 Pin 19) |
| MISO0 (SPI 0) | MCP2515 controller SPI data output connected to RPi GPIO09 (J3 pin 21) |
| SCLK0 (SPI 0) | MCP2515 controller SPI clock input connected to RPi GPIO11 (J3 pin 23) |
| CAN CE | MCP2515 controller SPI interface enable input |
| By default connected to GPIO08 (J3 pin 24) - JP1 jumper closed | |
| Optionally connected to GPIO07 (pin 26 of J3 connector) - Shorted jumper JP2 | |
| CAN INT | MCP2515 controller IRQ interrupt output connected to GPIO25 (pin 22 of J3 connector) |
All control signals are output on connector J1 (40-pin, compatible with Raspberry Pi boards) and on pin connector J2. The signal layout is shown in the figure below, additionally the signals on connector J2 are described on the bottom side of the KAmod RPI 485&CAN Hat board.
The CAN interface is implemented via the MCP2515 controller, a description of the operation of this system is available in the manufacturer's documentation.
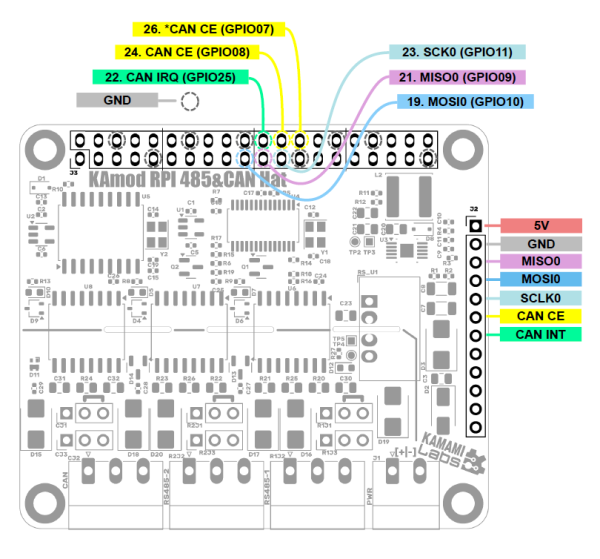
Power Supply
| Element | Function |
|---|---|
| Connector J1 PWR |
Optional power supply input adapted to a voltage in the range of 8...32 V. Powers the integrated switching regulator, which provides a voltage of 5 V with a capacity of up to 0.5 A, to power the components of the KAmod RPI 485&CAN Hat module. |
| Connector J2 |
Connector J2 provides 5V from the integrated regulator. It can be used as a power source for additional circuits or modules. The current consumption should not exceed 0.5A. |
| Connector J1 |
Connector J1 provides 5V from a base board, e.g. Raspberry Pi. This voltage is connected via a rectifier diode to the 5V power supply of the KAmod RPI 485&CAN Hat module, so the module is powered from the base board, but the module cannot supply power to the base board. |
| LED D12 | LED D12 lighting indicates power supply |
The KAmod RPI 485&CAN Hat module offers various power supply options:
- can be powered by 5V from a base board connected to connector J1, e.g. Raspberry Pi. No external power supply is required;
- can be powered by a voltage in the range of 8...32 V connected to connector J1 PWR. Then a stabilized voltage of 5 V is available on connector J2, but it does not power the base board connected to connector J1;
- can be powered by a stabilized voltage of 5 V connected to connector J2, but it does not power the base board connected to connector J1;
The layout of the connectors and contacts and their polarity are shown in the figure.
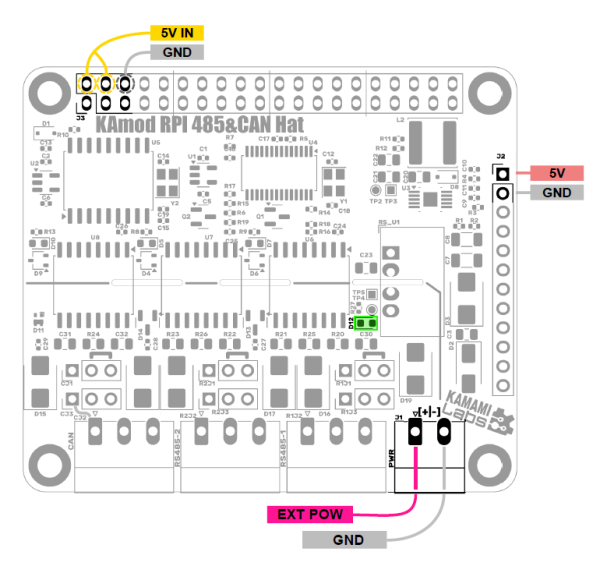
Indicator lights
| Indicator light | Function |
|---|---|
| D7 | The diode lights up to indicate data transmission/reception on the RS485-1 interface signal lines |
| D5 | The diode lights up to indicate data transmission/reception on the RS485-2 interface signal lines |
| D10 | The diode lights up to indicate data transmission/reception on the CAN interface signal lines |
| D12 | The diode lights up to indicate power supply |
The layout of the signaling lights on the KAmod RPI 485&CAN Hat board is shown in the figure.
Configuration of SPI CE signals
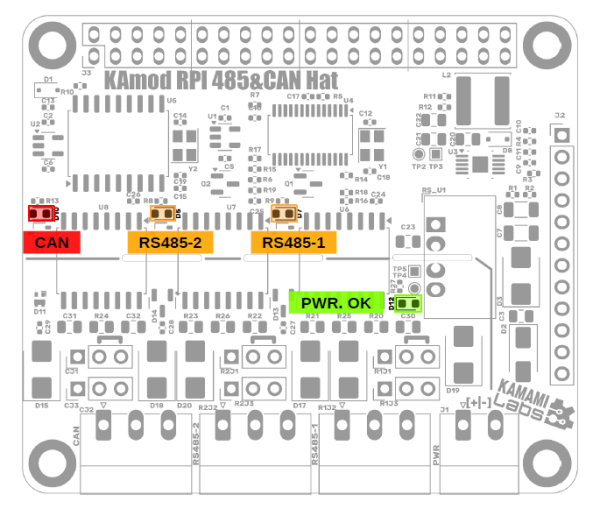
| Signal | Function | |
|---|---|---|
| CAN CE | Input activating the SPI interface of the MCP2515 controller | |
| By default connected to GPIO08 (pin 24 of J3 connector) | Shorted jumper JP1 | |
| Optionally connected to GPIO07 (pin 26 of J3) | Shorted jumper JP2 | |
| RS CE | Input activating the SPI interface of the SC16IS762 controller | |
| By default connected to GPIO07 (pin 26 of J3) | Shorted jumper JP3 | |
| Optionally connected to GPIO18 (pin 12 of J3) | Closed jumper JP4 | |
The KAmod RPI 485&CAN Hat module communicates with a base board, e.g. Raspberry Pi, via two SPI interfaces. The CE – Chip Enable signals of both interfaces can be connected in two configurations, depending on the setting of jumpers JP1...JP4, as described in the table above.
The jumpers are located on the bottom side of the module board, which is precisely illustrated in the figure below. By default, jumpers JP1 and JP3 are connected. In case of a configuration change, cut the connected jumpers and connect the appropriate jumpers using a soldering iron and a drop of solder.
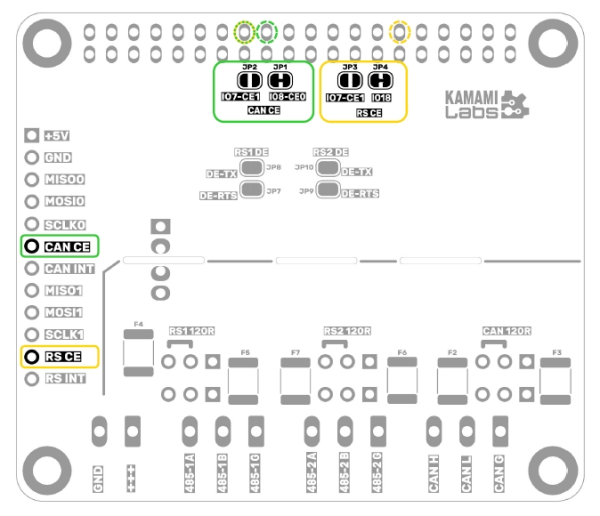
RS485 operating mode configuration
| Signal | Function | |
|---|---|---|
| RS1 DE | RS485-1 interface transceiver control signal | |
| By default, automatic TXD signal control is active | JP8 jumper closed | |
| Optionally, it is possible to control the RTS signal | Closed jumper JP7 | |
| RS2 DE | RS485-2 interface transceiver control signal | |
| By default, automatic TXD signal control is active | Closed jumper JP10 | |
| Optionally, it is possible to control the RTS signal | Closed jumper JP9 | |
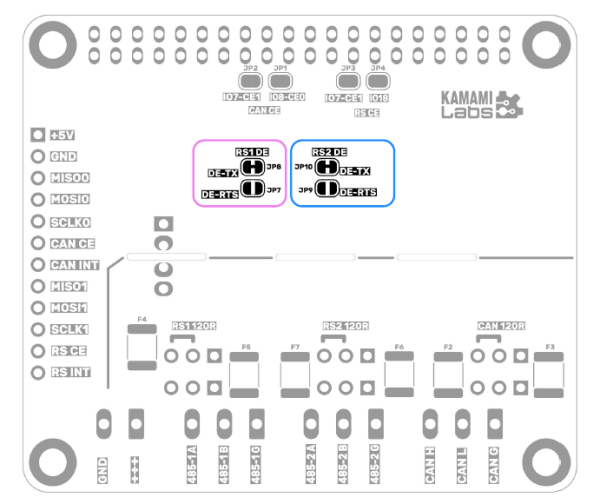
RS485 interface transceivers require a signal controlling the bus transmitter - activating the transmission mode. The control signal can be obtained from the data signal sent to the bus - TXD, or can be supplied independently - via the RTS line status. The KAmod RPI 485&CAN Hat module allows you to select one of these options for each of the RS485-1 and RS485-2 interfaces, by setting jumpers JP7...JP10, as described in the table above.
The jumpers are located on the bottom side of the module board, which is precisely illustrated in the figure below. By default, jumpers JP8 and JP10 are connected - automatic mode for both interfaces. In case of a configuration change, cut the connected jumpers and connect the appropriate jumpers using a soldering iron and a drop of solder.
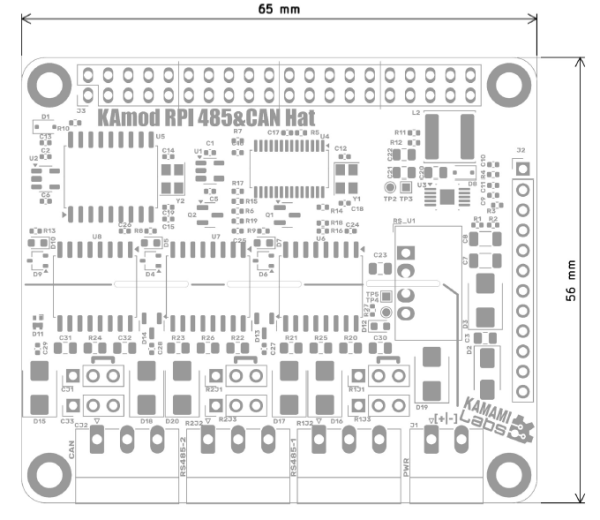
Dimensions
The dimensions of the KAmod RPI 485&CAN Hat board are 65x56 mm. The board height is about 15 mm, and the connector on the bottom side of the board, which fits the base board, is about 13 mm high.
Startup
Start Raspberry Pi 5 with the operating system installed on the memory card or other media. After the system desktop is displayed, open the console window (Terminal), e.g. using the Ctrl+Alt+T key combination and enter:
sudo nano /boot/firmware/config.txt
(in earlier versions of the operating system, the config.txt file was placed directly in the /boot directory)
In the file whose content we will see, remove the comment (remove the # sign) from the line:
dtparam=spi=on
However, if there is no such line, you should add it.
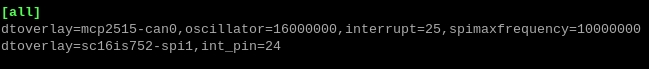
Then at the end of the file (scroll to the bottom with the arrows) add the following lines:
dtoverlay=mcp2515-can0,oscillator=16000000,interrupt=25,spimaxfrequency=10000000
and
dtoverlay=sc16is752-spi1,int_pin=24
Then save the changes using the Ctrl+O keys, close the editor using the Ctrl+X keys and restart the system, e.g. by entering the command:
sudo reboot
After the system desktop is displayed, open the console window (Terminal), e.g. using the Ctrl+Alt+T key combination and enter:
sudo dmesg | grep -i spi
If the previous steps were performed correctly, the following summary should be displayed:
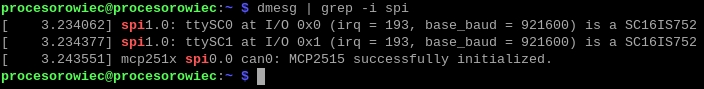
This means that both the SC16IS762 and MCP2515 controllers have been correctly installed in the system.
Testing the CAN interface requires entering 3 commands:
sudo ip link set can0 up type can bitrate 1000000 sudo ifconfig can0 up cansend can0 000#11.22.33.44
The D10 LED should flash, indicating activity on the CAN bus.
RS485 interfaces can be tested using the minicom, for RS485-1 enter:
minicom -D /dev/ttySC0
while for RS485-2 enter:
minicom -D /dev/ttySC1
The minicom program allows you to send characters entered from the keyboard and displays characters received via the selected RS485 interface. During the interface activity, the D5/D7 diodes will flash, but at high transmission speeds, e.g. 115200, the flashing of the LEDs will be barely noticeable.