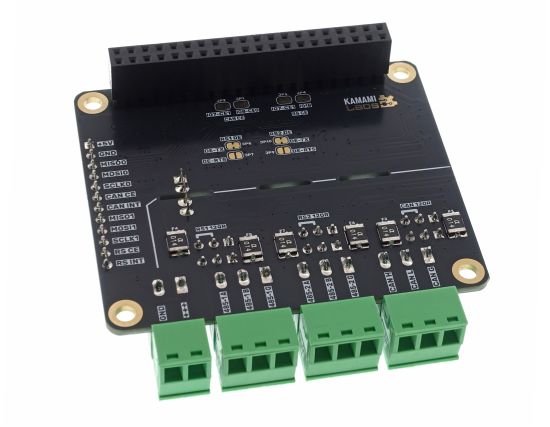
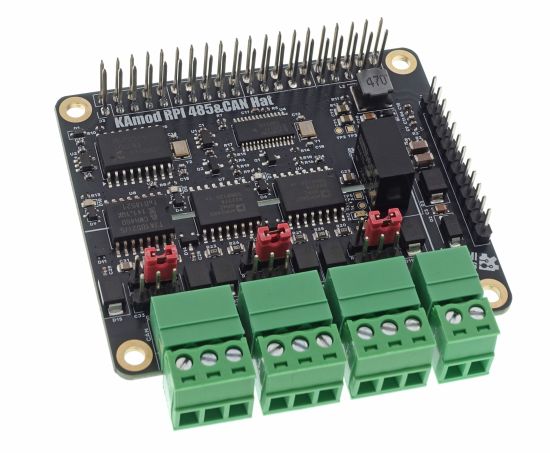
KAmod RPI 485 CAN Hat
From Kamamilabs.com - Wiki

Description
KAmod RPI 485&CAN Hat - Module with two RS485 interfaces and a CAN interface for Raspberry Pi
KAmod RPI 485&CAN Hat allows you to easily expand Raspberry Pi 5 computers with two RS485 interfaces and one CAN 2.0B interface. The interfaces contain extensive protection circuits and are galvanically isolated from the control circuits, which guarantees stable operation and resistance to interference and failures. The module has been designed to be compatible with Raspberry Pi series boards not only in version 5. It is controlled via 2 SPI interfaces, available on the 40-pin RPi connector, and in many other boards, e.g. Arduino, STM32, etc.
Basic features and parameters
- 2 RS485 interfaces – controlled by SC16IS752 controller (SPI→2xUART)
- 1 CAN 2.0B interface – controlled by MCP2515 controller (SPI→CAN)
- RS485 interfaces equipped with 2 isolated ADM2483 transceivers
- CAN interface equipped with isolated TJA1052 transceiver
- RS485 and CAN interfaces galvanically separated from control circuits
- Possibility to connect 120 Ω terminating resistors to each interface line
- Maximum RS485 interest communication speed: 500 kbps
- Maximum CAN interest communication speed: 1 Mbps
- Control via two SPI interfaces operating with 3.3 V voltage
- Automatic control of RS485 transceiver transmission direction
- Power supply 5 V/0.3 A taken from the Raspberry Pi board or from an additional source
- Optional power input adapted to a voltage in the range of 8...32 V
- Stabilized power output 5 V, max 0.5 A
- Easy installation on Raspberry Pi 5, also in the version with the RPi Active Cooler radiator
- Can work with many boards from the Raspberry Pi family and others equipped with SPI interfaces operating at a voltage of 3.3 V
- Module dimensions 65x56 mm, height approx. 15 mm (and a connector under the board with a height of approx. 13 mm)
Standard Equipment
| Code | Description |
|---|---|
| KAmod RPI 485&CAN Hat |
|
| Mounting Kit |
|

Block diagram
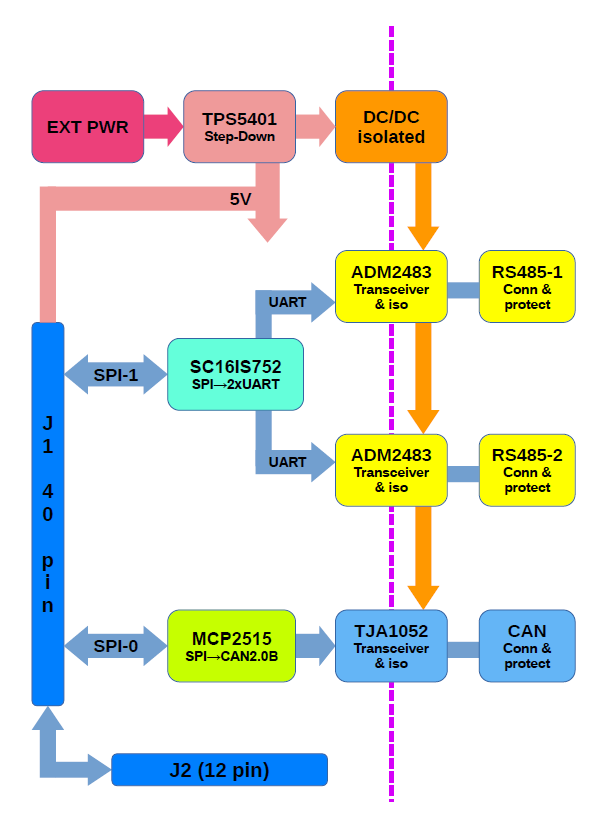
Circuit diagram
The circuit diagram of the KAmod RPI 485&CAN Hat module can be downloaded here: KAmod RPI 485&CAN Hat diagram
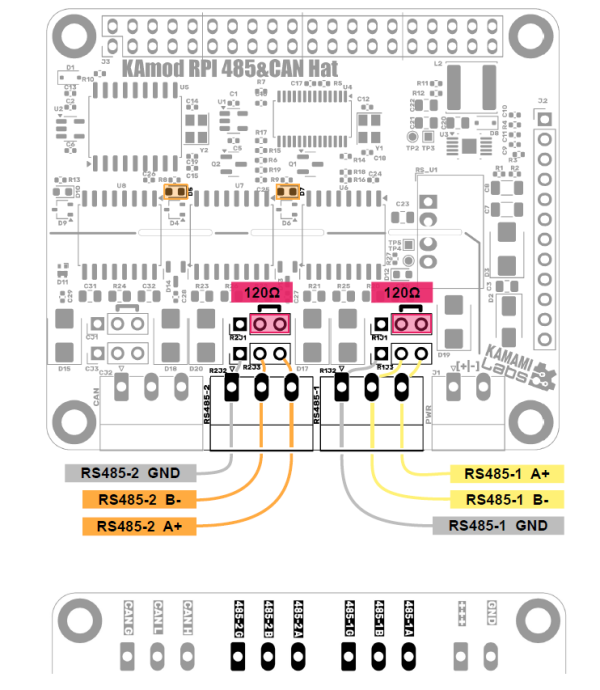
RS485 Interfaces
| Interface | Element | Function |
|---|---|---|
| RS485-1 |
Connector |
Connecting a 120 Ω terminating resistor to the RS485-1 bus line, |
|
Connector |
Main RS485-1 bus connector, pin 1 – GND; pin 2 – B(-); pin 3 – A(+) | |
|
Connector |
Additional RS485-1 bus connector, pin 1 – GND; pin 2 – B(-); pin 3 – A(+) | |
|
LED |
The diode lights up to indicate data transmission/reception on the RS485-1 interface signal lines | |
| RS485-2 |
Connector |
Connecting a 120 Ω terminating resistor to the RS485-2 bus line, |
|
Connector |
Main RS485-2 bus connector, pin 1 – GND; pin 2 – B(-); pin 3 – A(+) | |
|
Connector |
Secondary RS485-2 bus connector, pin 1 – GND; pin 2 – B(-); pin 3 – A(+) | |
|
LED |
The diode lights up to indicate data transmission/reception on the RS485-2 interface signal lines |
The RS485 interfaces are controlled by ADM2483 transceivers, which also provide galvanic separation between the control signals and the RS485 bus lines.
The bus lines are marked as: A(+), B(-) and GND ground and are available on the Phoenix MC connector (R1J2, R2J2) and on goldpin pins with a standard 2.54 mm pitch (R1J3, R2J3). Their arrangement is shown in the drawing and is described on the bottom side of the module board.
The RS485 bus lines are equipped with circuits protecting against overvoltages. Putting a jumper on pins 2-3 of RxJ1 allows you to connect a 120 Ω terminating resistor between lines A and B of the interface.
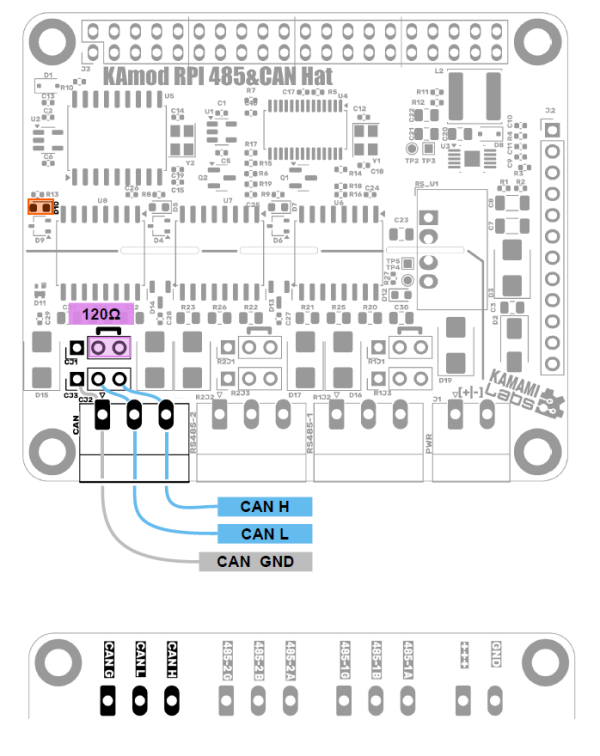
CAN Interface
| Interface | Element | Function |
|---|---|---|
| CAN |
Connector |
Connecting a 120 Ω terminating resistor to the CAN bus line, |
|
Connector |
Main CAN bus connector, pin 1 – GND; pin 2 – CAN L; pin 3 – CAN H | |
|
Connector |
Additional CAN interface connector,
pin 1 – GND; pin 2 – CAN L; pin 3 – CAN H | |
|
LED |
The diode lights up to indicate data transmission/reception on the CAN interface lines |
The CAN interface is controlled by a TJA1052 transceiver, which also provides galvanic separation between control signals and the CAN bus lines.
The bus lines are marked as: CAN H, CAN L and ground GND and are available on the Phoenix MC (CJ2) type connector and on goldpins (CJ3) with a standard 2.54 mm pitch. Their layout is shown in the drawing and is described on the bottom side of the module board.
The CAN bus lines are equipped with circuits that protect against overvoltages. Putting a jumper on pins 2-3 of CJ1 allows you to connect a 120 Ω terminating resistor between the CAN H and CAN L lines.
RS485 Control
| RS485 Interfaces | |
|---|---|
| Control Signal | Function |
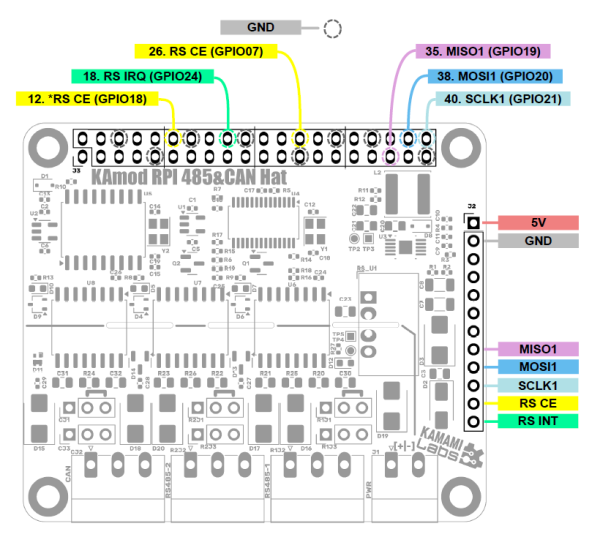
| MOSI1 (SPI 1) | SPI data input of SC16IS762 controller, connected to GPIO20 RPi (pin 38 of J3) |
| MISO1 (SPI 1) | SPI data output of SC16IS762 controller, connected to GPIO19 RPi (pin 35 of J3) |
| SCLK1 (SPI 1) | SPI clock input of SC16IS762 controller, connected to GPIO21 RPi (pin 40 of J3) |
| RS CE | SPI interface activation input of SC16IS762 controller |
| By default connected to GPIO07 (pin 26 of J3 connector) - Shorted jumper JP3 | |
| Optionally connected to GPIO18 (pin 12 of J3 connector) - Shorted jumper JP4 | |
| RS INT | SC16IS762 controller IRQ interrupt output connected to GPIO24 (pin 18 of J3 connector) |
All control signals are led out on connector J1 (40-pin, compatible with Raspberry Pi boards) and on pin header J2. The signal layout is shown in the figure below, additionally the signals on connector J2 are described on the bottom side of the KAmod RPI 485&CAN Hat board.
RS485 interfaces are implemented via the SC16IS762 controller, the description of this system is available in the manufacturer's documentation.
CAN Control
| CAN Interface | |
|---|---|
| Control Signal | Function |
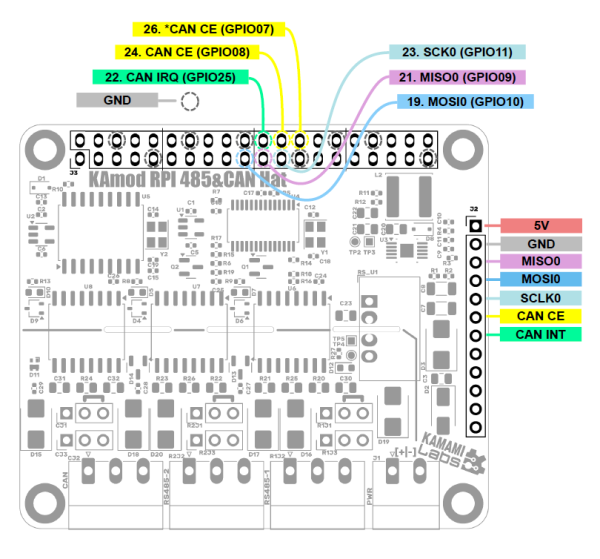
| MOSI0 (SPI 0) | MCP2515 Controller SPI Data Input Connected to GPIO10 RPi (J3 Pin 19) |
| MISO0 (SPI 0) | MCP2515 controller SPI data output connected to RPi GPIO09 (J3 pin 21) |
| SCLK0 (SPI 0) | MCP2515 controller SPI clock input connected to RPi GPIO11 (J3 pin 23) |
| CAN CE | MCP2515 controller SPI interface enable input |
| By default connected to GPIO08 (J3 pin 24) - JP1 jumper closed | |
| Optionally connected to GPIO07 (pin 26 of J3 connector) - Shorted jumper JP2 | |
| CAN INT | MCP2515 controller IRQ interrupt output connected to GPIO25 (pin 22 of J3 connector) |
All control signals are output on connector J1 (40-pin, compatible with Raspberry Pi boards) and on pin connector J2. The signal layout is shown in the figure below, additionally the signals on connector J2 are described on the bottom side of the KAmod RPI 485&CAN Hat board.
The CAN interface is implemented via the MCP2515 controller, a description of the operation of this system is available in the manufacturer's documentation.
Zasilanie
| Element | Funkcja |
|---|---|
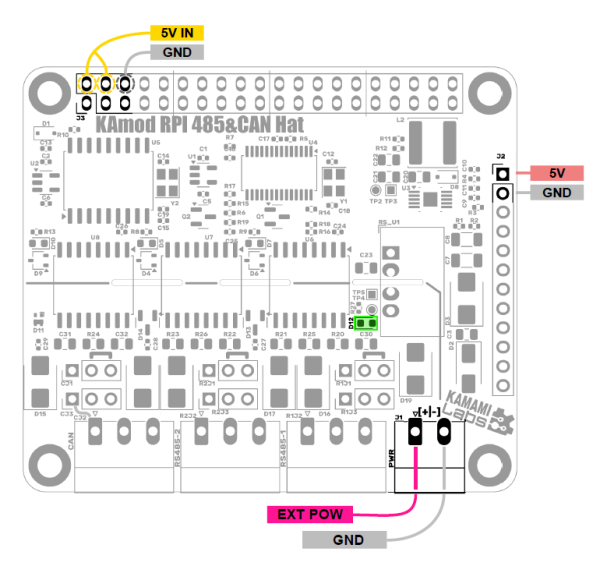
| Złącze J1 PWR |
Opcjonalne wejście zasilania dostosowane do napięcia z zakresu 8...32 V. Zasila zintegrowany stabilizator impulsowy, który dostarcza napięcia 5 V o wydajności do 0,5 A, do zasilania komponentów modułu KAmod RPI 485&CAN Hat. |
| Złącze J2 |
Na złączu J2 dostępne jest napięcie 5 V ze zintegrowanego stabilizatora. Może posłużyć jako źródło zasilania dla dodatkowych obwodów lub modułów. Pobór prądu nie powinien przekraczać 0,5 A. |
| Złącze J1 |
Na złączu J1 dostępne jest napięcie 5 V dostarczane z płytki bazowej, np. Raspberry Pi. Napięcie to jest połączone przez diodę prostowniczą z zasilaniem 5 V modułu KAmod RPI 485&CAN Hat, zatem moduł jest zasilany z płytki bazowej, ale moduł nie może dostarczać zasilania do płytki bazowej. |
| Dioda LED D12 | Świecenie diody LED D12 oznacza obecność zasilania |
Modułu KAmod RPI 485&CAN Hat oferuje różne opcje zasilania:
- może być zasilany napięciem 5V z płytki bazowej dołączonej do złącza J1, np. Raspberry Pi. Nie jest wymagane zewnętrzne zasilanie;
- może być zasilany napięciem z zakresu 8...32 V dołączonym do złącza J1 PWR. Wtedy stabilizowane napięcie 5 V jest dostępne na złączu J2, ale nie zasila ono płytki bazowej dołączonej do złącza J1;
- może być zasilany napięciem stabilizowanym 5 V dołączony do złącza J2, ale nie zasila ono płytki bazowej dołączonej do złącza J1;
Rozmieszczenie złącz i styków oraz ich polaryzację pokazano na rysunku.
Kontrolki sygnalizujące
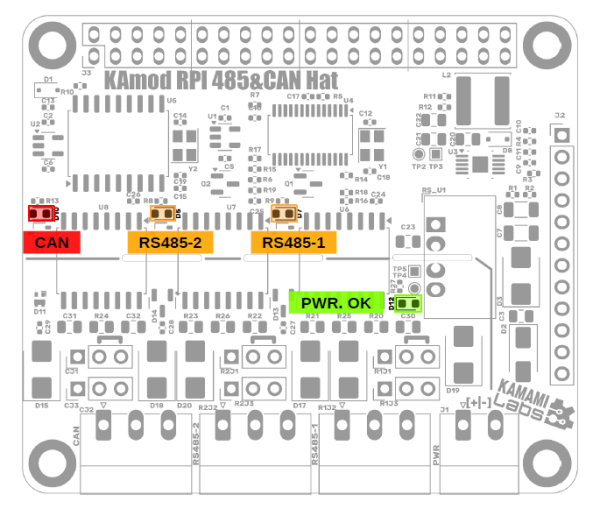
| Kontrolka | Funkcja |
|---|---|
| D7 | Świecenie diody sygnalizuje nadawanie/odbieranie danych na liniach sygnałowych interfejsu RS485-1 |
| D5 | Świecenie diody sygnalizuje nadawanie/odbieranie danych na liniach sygnałowych interfejsu RS485-2 |
| D10 | Świecenie diody sygnalizuje nadawanie/odbieranie danych na liniach sygnałowych interfejsu CAN |
| D12 | Świecenie diody oznacza obecność zasilania |
Rozmieszczenie kontrolek sygnalizacyjnych na płytce KAmod RPI 485&CAN Hat zostało pokazane na rysunku.
Konfiguracja sygnałów SPI CE
| Sygnał | Funkcja | |
|---|---|---|
| CAN CE | Wejście aktywujące interfejs SPI kontrolera MCP2515 | |
| Domyślnie połączone do GPIO08 (pin 24 złącza J3) | Zwarta zwora JP1 | |
| Opcjonalnie połączone do GPIO07 (pin 26 złącza J3) | Zwarta zwora JP2 | |
| RS CE | Wejście aktywujące interfejs SPI kontrolera SC16IS762 | |
| Domyślnie połączone do GPIO07 (pin 26 złącza J3) | Zwarta zwora JP3 | |
| Opcjonalnie połączone do GPIO18 (pin 12 złącza J3) | Zwarta zwora JP4 | |
Moduł KAmod RPI 485&CAN Hat realizuje komunikację z płytką bazową np. Raspberry Pi poprzez dwa interfejsy SPI. Sygnały CE – Chip Enable, obu interfejsów mogą być połączone w dwóch konfiguracjach, w zależności od ustawienia zworek JP1...JP4, tak jak opisano w powyższej tabeli.
Zworki są umieszczone na dolnej stronie płytki modułu, co dokładnie obrazuje poniższy rysunek. Domyślnie połączone są zworki JP1 i JP3. W przypadku zmiany konfiguracji należy rozciąć połączone zworki i połączyć odpowiednie zworki za pomocą lutownicy i kropli spoiwa lutowniczego.
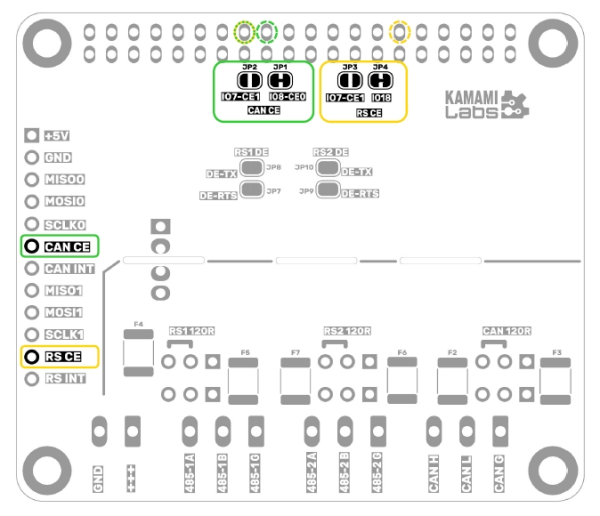
Konfiguracja trybu pracy RS485
| Sygnał | Funkcja | |
|---|---|---|
| RS1 DE | Sygnał sterujący transceiverem interfejsu RS485-1 | |
| Domyślnie aktywne jest automatyczne sterowanie sygnałem TXD | Zwarta zwora JP8 | |
| Opcjonalnie możliwe jest sterowanie sygnałem RTS | Zwarta zwora JP7 | |
| RS2 DE | Sygnał sterujący transceiverem interfejsu RS485-2 | |
| Domyślnie aktywne jest automatyczne sterowanie sygnałem TXD | Zwarta zwora JP10 | |
| Opcjonalnie możliwe jest sterowanie sygnałem RTS | Zwarta zwora JP9 | |
Transceivery interfejsów RS485 wymagają sygnału sterującego nadajnikiem magistrali -aktywującego tryb nadawania. Sygnał sterujący może być uzyskiwany z sygnału danych wysyłanych na magistralę - TXD, lub może być doprowadzany niezależnie – poprzez stan linii RTS. Moduł KAmod RPI 485&CAN Hat pozwala na wybranie jednej z tych opcji dla każdego z interfejsów RS485-1 i RS485-2, poprzez ustawienie zworek JP7...JP10, tak jak opisano w powyższej tabeli.
Zworki są umieszczone na dolnej stronie płytki modułu, co dokładnie obrazuje poniższy rysunek. Domyślnie połączone są zworki JP8 i JP10 – tryb automatyczny dla obu interfejsów. W przypadku zmiany konfiguracji należy rozciąć połączone zworki i połączyć odpowiednie zworki za pomocą lutownicy i kropli spoiwa lutowniczego.
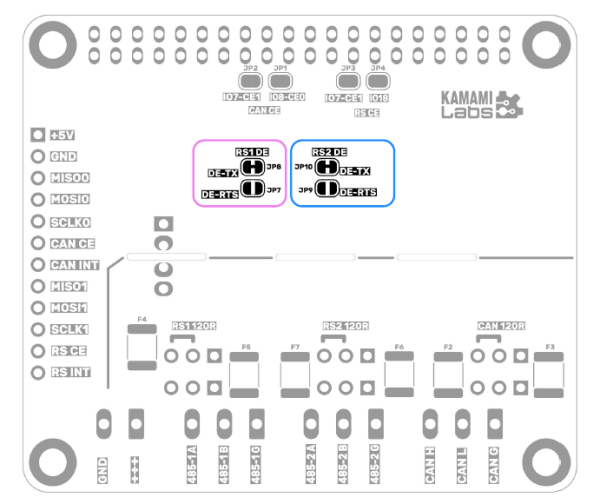
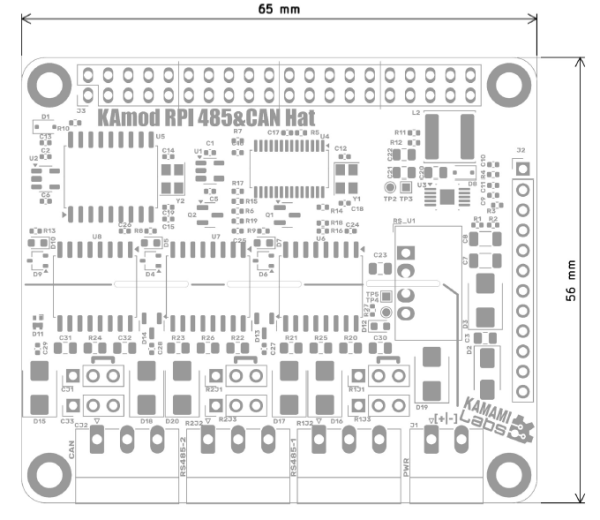
Wymiary
Wymiary płytki KAmod RPI 485&CAN Hat to 65x56 mm. Wysokość płytki to ok. 15 mm, dodatkowo złącze na dolnej stronie płytki, pasujące do płytki bazowej, ma wysokość ok 13 mm.
Uruchomienie
Uruchamiamy Raspberry Pi 5 z systemem operacyjnym zainstalowanym na karcie pamięci lub innym, nośniku. Po wyświetleniu pulpitu systemu otwieramy okno konsoli (Terminal) np. za pomocą kombinacji klawiszy Ctrl+Alt+T i wpisujemy:
sudo nano /boot/firmware/config.txt
(we wcześniejszych wersjach systemu operacyjnego plik config.txt był umieszczony bezpośrednio w katalogu /boot)
W pliku, którego treść zobaczymy, należy usunąć komentarz (usunąć znak #) z linii:
dtparam=spi=on
Natomiast, jeżeli takiej linii nie ma to należy ją dopisać.
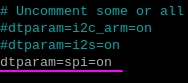
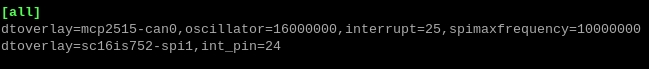
Następnie na końcu pliku (przewijamy strzałkami do samego dołu) należy dopisać linie:
dtoverlay=mcp2515-can0,oscillator=16000000,interrupt=25,spimaxfrequency=10000000
oraz
dtoverlay=sc16is752-spi1,int_pin=24
Następnie należy zapisać zmiany za pomocą klawiszy Ctrl+O, zamknąć edytor za pomocą klawiszy Ctrl+X i uruchomić system ponownie, np. wpisując polecenie:
sudo reboot
Po wyświetleniu pulpitu systemu otwieramy okno konsoli (Terminal) np. za pomocą kombinacji klawiszy Ctrl+Alt+T i wpisujemy:
sudo dmesg | grep -i spi
Jeśli wcześniejsze etapy zostały wykonane prawidłowo powinno pokazać się takie podsumowanie:
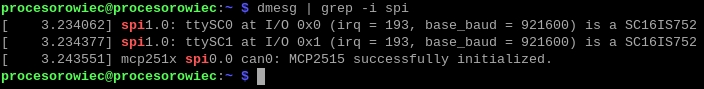
Oznacza to, że zarówno kontroler SC16IS762, jak i MCP2515 zostały prawidłowo zainstalowane w systemie.
Przetestowanie interfejsu CAN wymaga wpisania 3 komend:
sudo ip link set can0 up type can bitrate 1000000 sudo ifconfig can0 up cansend can0 000#11.22.33.44
Powinna migać dioda LED D10 sygnalizująca aktywność na magistrali CAN.
Interfejsy RS485 można przetestować z użyciem programu minicom, dla RS485-1 należy wpisać:
minicom -D /dev/ttySC0
natomiast dla RS485-2 należy wpisać:
minicom -D /dev/ttySC1
Program minicom pozwala wysyłać znaki wpisywane z klawiatury oraz wyświetla znaki odebrane przez wybrany interfejs RS485. W czasie aktywności interfejsów będą migały diody D5/D7, ale przy znacznych prędkościach transmisji, np. 115200, miganie diod LED będzie ledwo zauważalne.